As the countries evolved, it’s the paper currency that has been dictating the world, causing rise and fall of economies, and sometimes even leading to cold wars.
Now, it seems the time has come for another strategic shift in the world economy, and ‘digital trend’ is the driving factor this time!
Emerging technology trends and the digital revolution gave rise to the concept of digital currency or cashless economy, which has been under debate for years, globally.
While some countries are favorable to a cashless economy, some are still against it owing to regulatory and other perennial challenges like cybersecurity, which is the opposite side of digital currency.
However, the path to the cashless trend is very clear now! The rise of mobile usage, digital applications like UPI, digital payment platforms, and the increasing usage of e-wallets make this evident.
[Also Read: India, Singapore Deepening Ties in Digital Economy]
Cashless Economy: Definition, Types and Benefits
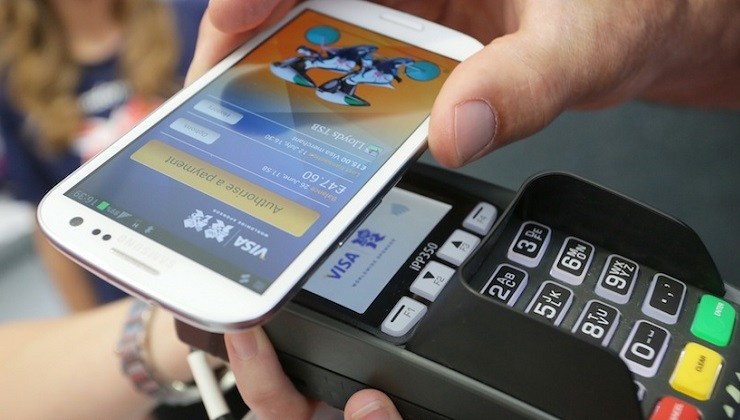

By definition, the cashless economy refers to the flow of currency through electronic channels such as debit/credit cards, internet banking, mobile banking, Point of Sales (POS) and e-wallets.
The cashless economic activity usually happens in three different modes, namely:
- Mobile or e-wallet
- Plastic money
- Net Banking
While Mobile Wallet refers to the usage of mobile wallets or digital payment apps, Plastic Money involves the usage of debit/credit cards across swiping machines and POS terminals.

The other form is Net Banking, wherein the user logs in to the banking account and make the transactions through National Electronic Fund Transfer (NEFT), Real Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) or Immediate Payment Service (IMPS) (in case of India).
The next level was the rise of bitcoins and cryptocurrencies, which are popularly termed as virtual currencies. More in the offing!
Cashless Over Cash-based Economy

The most common reason driving the demand for the cashless economy is an ease in transactions and maintenance.
The increased digitization makes the transactions simplified and easier than ever, along with improved connectivity among users.
It’s evident in transactions that involve big money transfers happening in no time at a matter of finger touch.
Moreover, a cashless economy is also viewed as an effective means to tackle black money. It helps curb the circulation of fake currency notes, as every online transaction can be strictly monitored guided by regulatory mechanisms.
This will also help governments tackle tax evasions as every record is stored digitally and can be traced easily.
A cashless system can also be advantageous given the risks associated with carrying huge cash, which can be physical damage or theft.
Moreover, the cashless system can also avoid the utilization of natural resources like paper, printing machines, personnel and power, which are the prerequisites for making paper currency.
So, a cashless economy maintains an edge over cash-based one, while offering more transparency and accountability.
However, cybersecurity risks continue to challenge the rise of digital of cashless currency.
There are also a wide range of debates around expert opinions that governments and companies get more benefited than individuals in a cashless society, by levying fees on every mode of transaction.
Countries That Made’ Cashless Society’ Possible

Despite debates and controversies, countries like Sweden, China and the UK have proved that the cashless society is possible.
Sweden reportedly has more 85 percent of its transactions happening online and only 2 percent involving cash, thus inching closer to a cashless economy.
Surprisingly, 50 percent of the country’s population using a digital payment app called Swish, and adding to that, majority of the country’s retailers don’t accept cash.
China also has such game-changing digital payment apps run by popular company Alibaba Group. Here, majority transactions happen through QR code scanning. However, the country is not that favorable for credit-based transactions.
Coming to the UK, the country has already set an example for card-based transactions and is promoting contactless payments. Around 50 percent of the country’s in-store transactions happen contactless.
According to Mastercard, entire Europe has seen a 97 percent rise in demand for contactless payments.
The World’s Most Cashless Countries (Infographic)
 Source: Forexbusiness.org
Source: Forexbusiness.org
Then coming to the superpower US, the cashless society is far from reality with the cashless system facing severe regulatory challenges in the majority of US states. Moreover, 70 percent of US consumers still prefer cash-based transactions for their regular buying or selling activity.
How About India? A Glance at Cashless Trend in India!

India has a special love for cash in line with the world’s top-10 highly cash-reliant countries like Chad, Angola, Ethiopia, Tanzania, Nepal and Iran.
However, the country is no exception to the cashless trend and in fact, on the verge of increasing adoption through supportive government schemes like Digital India.
Resultant is what we see today in the Indian society, the sudden rise in demand for the online marketplace and the increasing usage of UPI, JioMoney, G-Pay, Paytm, PhonePe, AmazonPay, Paypal, among other digital payment apps.
The Modi Government’s demonetization decision to curb black money menace has proved this is possible in India and has been one primary driver to the rising cashless trend in India.
Post the demonetization of high-value currency notes, the country has reportedly seen a 55 percent rise in its overall digital transactions, with mobile banking alone rising by a whopping 122 percent.
In 2016-17, the year demonetization was announced, the cost of printing currency notes was Rs. 79.65 billion.
Post the ban of high-value currency notes, the printing cost saw a sudden decline to Rs. 49.12 billion in the very next fiscal year (2017-18).
Since then, the Indian Government has also been encouraging cashless society like never in the past, giving the digital currency a new hope.
Programs like Pradhan Mantri Jan-Dhan Yojna (PMJDY) and Digital India have been successful in bringing more people under cover of new-age connectivity and advanced banking.

Increasing mobile usage, rising internet speeds, fast-spreading awareness and affordable data plans are among other key drivers by driving the cashless trend in India.
Meanwhile, a special committee formed by RBI under Nandan Nilekani’s monitor is working on plans for usage of the digital payment process in settling remittance transactions and helping residents when they travel abroad.
“This is like Chinese users being able to use WeChat in many jurisdictions,” says Nilekani’s panel said in a statement.
If this is implemented, India will also have a common digital payment platform like other economies striving for a cashless society.
[Also Read: ‘No’ To Cash, Govt Promotes ‘Digital Payments’!]
This will naturally increase the competition among different players in the digital payment field, intensifying the demand further.
Nilekani’s panel is reportedly working on ways to improve India’s annual per capita digital transactions from 22 (currently) to 220 by March 2021.
More amazing plans must be in the offing to drive the cashless trend in India, provided equal support exists from the regulatory bodies.
Let’s see what happens!
More Articles:
- National Education Policy (NEP) 2020
- Profitable Business Ideas in India
- Nepotism in India
- What is The New Farm Bill 2020?